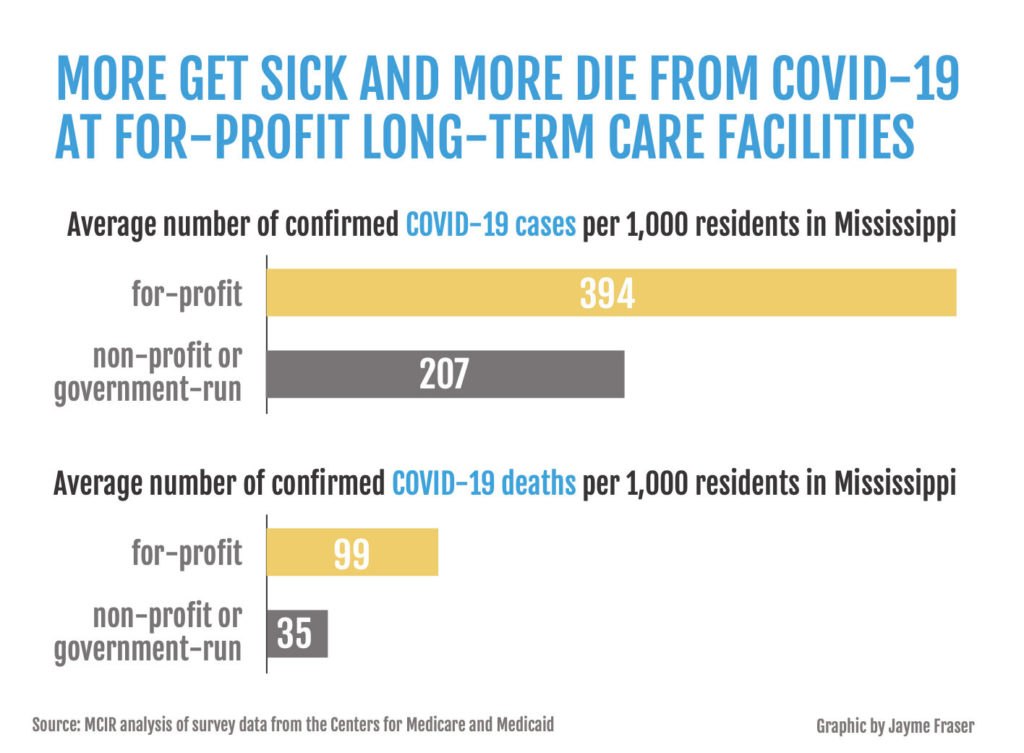
Twice as many residents caught COVID-19 at Mississippi’s for-profit nursing homes than in public or nonprofit homes, and nearly three times more died in the private facilities, the Mississippi Center for Investigative Reporting found in an analysis of health data.
Four in 10 residents was the average number of confirmed COVID-19 cases in those for-profit long-term-care facilities. One possible factor: The federal Occupational Safety and Health Administration had already cited 80% of Mississippi’s nursing homes for infection-control problems before the pandemic hit.
Charlene Harrington, a professor emeritus at the University of California at San Francisco who discovered similar results in a just-released study of nursing homes in California, said the current pandemic is exposing problems that have persisted for decades. “We’ve just looked the other way for 30 years,” she said.
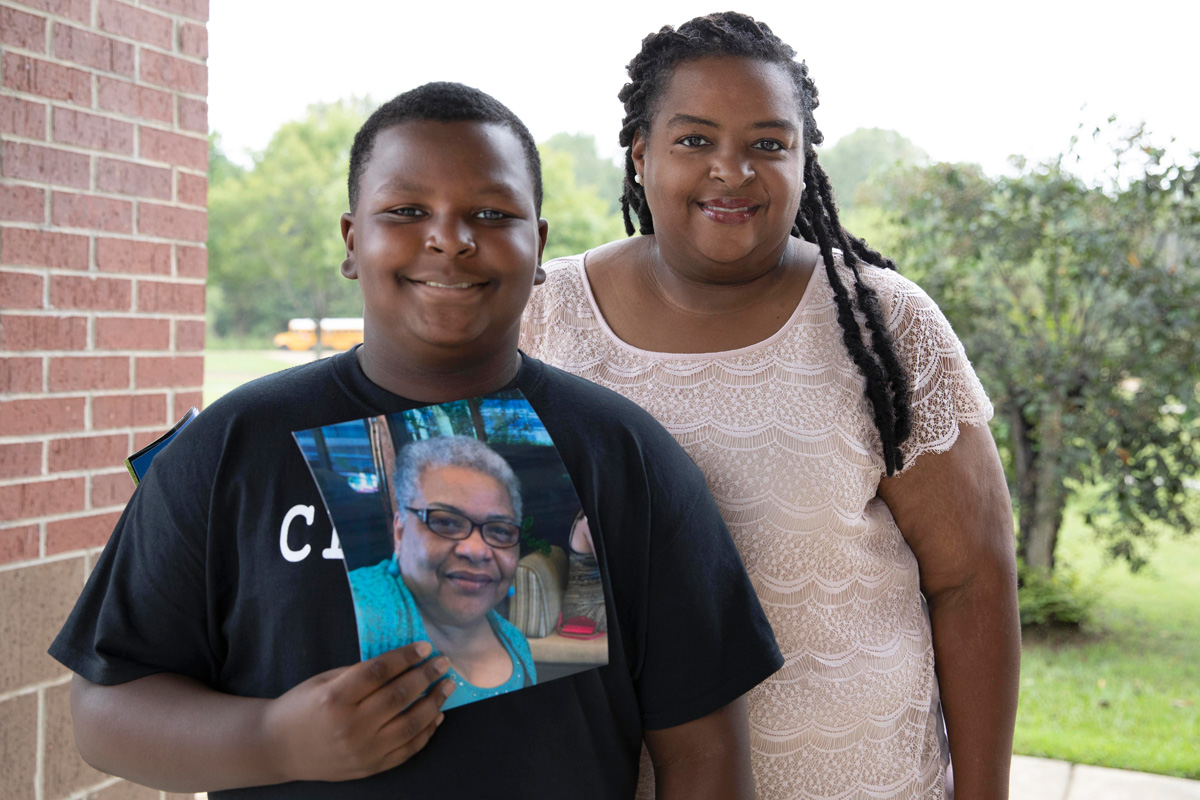
OSHA has been investigating three nursing homes in Mississippi, all of them for-profit, for workplace catastrophes or fatalities, including Lakeside Health & Rehabilitation Center in Quitman in Clarke County south of Meridian. One of the home’s nursing assistants, Carole Faye Doby of Stonewall, died of COVID on May 15, and two residents also died of the disease.
At least a week before she contracted the coronavirus, Doby warned her family that “things were getting bad at the nursing home, and that we didn’t need to come around,” her daughter, Shenika Jackson of Clinton, recalled. She said her mother shared that a fellow worker and a resident (who later died) had both come down with the disease.
On May 6, Doby was tested for COVID. “We did see her on Sunday, Mother’s Day. We sat outside the porch and ate lunch. She was inside the window,” Jackson said.
By May 11, her mother still did not have results and continued to get sicker so she saw a doctor, who had Doby rushed to the hospital by ambulance, Jackson said. Because of COVID, she could not visit with her family, except by way of video calls on her smartphone, Jackson said.
On May 15, four days after Doby entered the hospital, doctors placed her on a ventilator. Hours later, she died, less than a month after she had celebrated her 63rd birthday. Jackson said the news stunned her and the rest of her family because her mother was “very healthy.”
From May through Sept. 6, federal data show 86 COVID cases that led to the deaths of six residents and one staff member at the facility.
Clarke County Facility ‘Much Below Average’
Last month, Jackson said an OSHA investigator contacted her and asked if her mother could have contracted the disease elsewhere. Jackson replied no, saying the only places her mother went were to work and home.

Since 2017, the 120-bed Clarke County nursing home has been cited for seven deficiencies, and has also been fined $13,868. Medicare ranked the home “much below average.”
In 2019, a licensed practical nurse was caught using a device to measure blood sugar on different residents without disinfecting it, risking the spread of blood-borne diseases and placing the resident in “immediate jeopardy,” the Medicare report stated. Asked why she had not cleaned the glucometer, the nurse “shrugged her shoulders and stated she did not even think about doing it,” the report said.
A Pensacola, Fla., company, Gulf Coast Health Care, owns Lakeside, seven other homes in Mississippi and 34 homes in Florida. One Mississippi home, Dixie White House Health and Rehabilitation Center in Pass Christian in Harrison County on the Gulf Coast, saw 30 residents and 15 staff contract COVID, the latest federal data show, despite having only 55 beds. Four residents died.
Most of these Mississippi homes have a poor record. Four have been fined a total of $67,567, including the 60-bed Singing River Health and Rehabilitation Center in Moss Point, in Jackson County, which has seen 56 cases of COVID among residents and staff members as well as five deaths. In recent years, the home has suffered 25 deficiencies and has been fined $31,831.
Gulf Coast Health Care officials did not respond to repeated messages.
Facilities Ground Zero For Pandemic
Long-term-care facilities have become ground zero for the pandemic in the U.S. with about 40% of the deaths, despite having only 7% of the cases. Of the more than 200,000 deaths so far, more than 77,000 are of residents and staff members at nursing homes.
“There is no excuse for having that many deaths,” said Harrington, who has studied long-term-care facilities for decades. “Nursing homes are less than one-half of 1% of the population, and yet they’re accounting for all these deaths.”
In Mississippi, these deaths have surpassed 1,200 residents, not counting at least 27 staff members who all died from COVID-19 they contracted at for-profit homes since May. Despite such grim numbers, most of the state’s homes are not testing asymptomatic staff and residents as part of a surveillance program because operators say they lack personal protective equipment, supplies, trained personnel, access to a laboratory or other basic medical tools.
When COVID hit, policymakers and political leaders focused on keeping hospital patients safe, but neglected those inside these facilities, Harrington said: “If these nursing homes had had the right staffing and had PPE and had enforcement of what nursing homes should be doing, we wouldn’t have had all these deaths.”
Federal officials say they have saved lives.
“The Trump Administration’s effort to protect the uniquely vulnerable residents of nursing homes from COVID-19 is nothing short of unprecedented,” Seema Verma, administrator for the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, or CMS, said in a statement.
CMS convened an independent coronavirus commission, which delivered its report in September. Verma said these findings represent “a resounding vindication of our overall approach to date.”
The report concluded that the pandemic “has exposed and exacerbated” long-standing problems in nursing homes with many people believing the nation’s “patchwork approach to infection prevention and control” has played a role in “our nation’s inability to contain the spread of the virus.”
OSHA Investigates Mississippi Nursing Homes
OSHA has also investigated Bedford Care Center of Hattiesburg, in Forrest County, for a catastrophe or workplace fatality. The facility has seen 43 COVID cases and the deaths of 13 residents and one staff member, federal data show.
Since 2017, the 152-bed nursing home has faced citations for 15 deficiencies and fined $6,500. Medicare concluded the home was “much below average,” detailing the escape of a resident because a receptionist was busy on her cell phone.
A limited-liability corporation of the same name owns Bedford in Mississippi, its Mississippi Secretary of State filing shows. There are seven other Bedford Care Centers across the state.
Bedford Care Center did not respond to repeated requests for comment.
In June, OSHA began investigating Diversicare of Brookhaven, in Lincoln County, for a catastrophe or workplace fatality. The nursing home has seen 60 cases and the deaths of 10 residents and one staff member, federal data show.
Since 2017, the 58-bed nursing home has drawn citations for nine deficiencies that included aides failing to wash or sanitize hands or use gloves. Medicare graded the home “above average.” A limited-liability corporation named Diversicare Leasing Company based in Brentwood, Tenn., owns Diversicare of Brookhaven as well as 10 others in the state, the Mississippi Secretary of State’s site shows. Diversicare did not respond to requests for comment.
In August, OSHA began investigating Starkville Manor Health Care and Rehabilitation Center, which Medicare has ranked “much below average.” Since 2017, the 119-bed nursing home in Oktibbeha County has seen 82 COVID cases and the deaths of 11 residents and one staff member. The home has also been cited for 17 deficiencies and fined $13,627.
The Centennial HealthCare Holding Company of Atlanta owns Starkville Manor, itsMississippi Secretary of State filing shows. Starkville Manor officials told MCIR they do not comment on investigations.
The company also owns The Oaks Rehabilitation and Healthcare Center in Meridian, which ranked “much below average” and was fined $22,874 for violations last year. Although the Lauderdale County facility has only 82 beds, it saw 48 COVID cases as well as the deaths of 30 residents and three staff members.
For-Profit Homes Suffer From Worse Staffing
Staffing at for-profit nursing homes runs well below the levels of nonprofit or government homes.
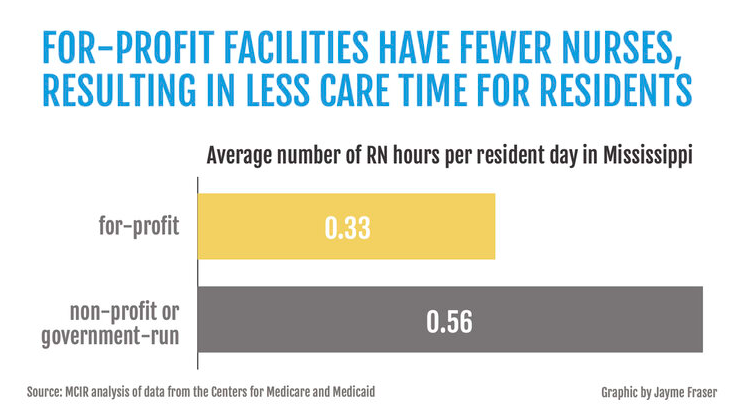
Nationwide, for-profit facilities schedule registered nurses to work an average of 26 minutes per resident each day, which is 40 minutes at nonprofit and government-run homes. That’s a difference of 34%.
In Mississippi, the level of care is lower, and the gap is even larger. For-profit facilities schedule registered nurses to work an average of 20 minutes per resident each day compared to 34 minutes at nonprofits, translating into a 41% difference.
Harrington said lack of personnel hurts the quality of care. A new study shows that nursing homes with lower staffing levels are seeing higher numbers of COVID cases and deaths. She said nursing homes “have been allowed to get away with it because states don’t have adequate monitoring. States have been complicit in not insisting on higher staffing.”
Black Death Rate Higher In State’s Nursing Homes
MCIR’s analysis shows that Mississippi nursing homes with a higher percentage of Black residents had higher rates of COVID cases and deaths. In facilities where half or more of the residents are Black, the homes have seen 55% more cases and 37% more deaths than in homes where Black residents accounted for less than 23% of the residents.
These results coincide with a just-released study on COVID in Connecticut nursing homes that shows “nursing homes with lower quality ratings and caring predominantly for Medicaid or racial and ethnic minority residents tend to have more confirmed cases in multivariable analyses.”
A previous study found that Black residents and other people of color tend to be cared for in facilities with limited clinical and financial resources, low nurse staffing levels and a relatively high number of care deficiency citations compared to white residents. The death rate for majority-Black nursing homes was more than 20% higher than in majority-white facilities, a Washington Post analysis of data from nearly three-fourths of the nation’s nursing homes found. In homes that were 70% or more Black, the death rate was 40% higher.
Many nursing homes are poorly designed, packing up to four residents in a room, where they share one bathroom, Harrington said. When COVID came, these homes failed to separate residents to keep them safe, she said. “Naturally, the staff got it, and so did the roommates.”
The pandemic has exposed the horrors of what is happening inside these homes, she said. “Who wants to be put in a nursing home and get such terrible care?”
As a result, these homes have become the haven for the impoverished, “a place of default for people who are poor,” she said. “They don’t have families to take care of them.”
Residents with families who want to visit have often died alone due to the high infection risk precluding family visits. “It’s really been sad.”
The Poverty & the Pandemic is a continuing series from the Mississippi Center for Investigative Reporting and the Pulitzer Center that captures the stories of people and places hit hardest by the nation’s worst pandemic in a century.
_____
Nursing Home PAC Spent Big Lobbying Mississippi Officials, Giving To Campaigns





